How would you measure the progress of a country’s development? For Tanzania, looking at the literacy rate offers valuable insights. Tanzania’s literacy rate has seen significant improvement over the years, painting a hopeful picture for its future.
Historically, educational access in Tanzania was limited. However, recent statistics indicate that the literacy rate among adults is approximately 77%. This achievement highlights the nation’s relentless efforts to enhance educational infrastructure and quality. Together, these advancements contribute to a more educated and capable populace.
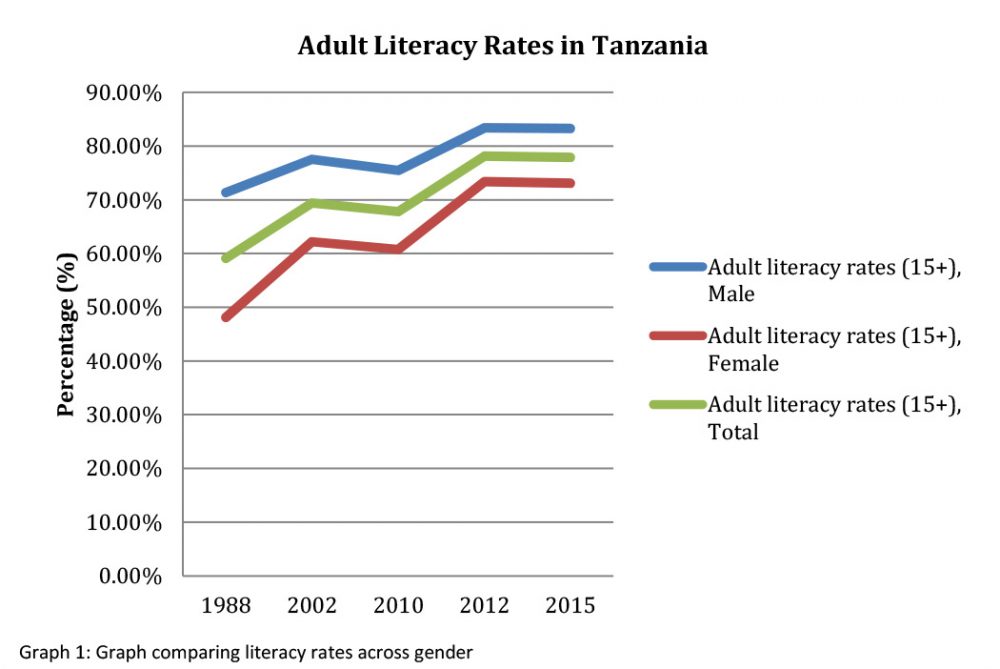
Overview of Literacy Rates in Tanzania
The literacy rate in Tanzania reflects the nation’s progress in education. Roughly 77% of adults in Tanzania can read and write. This figure has seen significant growth over the past few decades. Rural areas still face challenges in accessing quality education. Nonetheless, efforts to improve literacy rates continue nationwide.
Comparing literacy rates between genders shows that more men are literate than women. According to recent data, around 83% of men are literate, compared to 73% of women. These figures highlight the gender disparity in education. Special programs aim to bridge this gap. Further investments in female education are essential for balanced progress.
Among the youth, the literacy rate is significantly higher. About 86% of individuals aged 15-24 can read and write. This increase is largely due to improved primary education. Access to secondary education still needs improvement. Nevertheless, the future looks promising as more young people gain literacy skills.
Given the diverse challenges, the Tanzanian government collaborates with various organizations. These include international agencies and local NGOs. Their efforts focus on building more schools and providing better teacher training. Additionally, community awareness programs stress the importance of education. Together, these initiatives help uplift the nation’s overall literacy rates.
Understanding the Key Metrics and Trends
Examining key literacy metrics in Tanzania reveals several fascinating trends. One of the primary measurements is the literacy rate among adults versus youth. While approximately 77% of adults are literate, about 86% of young people aged 15-24 can read and write. This difference indicates recent improvements in access to education. Such trends underscore the country’s progress in addressing educational gaps.
Economic factors also play a significant role in literacy rates. Families in urban areas often have better access to educational resources compared to those in rural regions. Consequently, rural areas face more profound challenges in achieving high literacy levels. However, initiatives to build more schools and train teachers in these areas aim to improve the situation. These efforts are crucial for closing the urban-rural education divide.
The gender gap in literacy is another critical metric. Currently, around 83% of males are literate compared to 73% of females. This disparity can be traced to various socio-economic factors. Gender-specific programs and policies aim to ensure equal educational opportunities for boys and girls. Overcoming this gap remains a priority for sustainable development.
Government and non-governmental organizations collaborate to track and improve literacy metrics. Their strategies often involve a combination of data collection, policy implementation, and community engagement. Such coordinated efforts aim to create a more literate and educated population. By understanding these metrics and trends, policymakers can better address the country’s educational needs.
Factors Influencing Literacy in Tanzania
Several factors impact literacy rates in Tanzania, with the primary one being economic status. Families with limited financial resources often struggle to afford education-related costs. This challenge is more pronounced in rural areas, where poverty is more widespread. As a result, children from these families may not attend school regularly. Addressing economic barriers is crucial for improving literacy rates.
Another significant factor is access to quality education. In many rural parts of Tanzania, schools are sparsely located, making it difficult for children to attend. The shortage of trained teachers also affects the quality of education. According to the article, improving infrastructure and teacher training can help combat these challenges. Efforts are underway to build more schools and provide better resources.
Cultural practices also play a role in influencing literacy rates. In some communities, traditional beliefs may prioritize immediate work over education. This is particularly true for girls, who may be encouraged to marry young rather than continue their education. Community awareness programs aim to change these perceptions. Promoting the value of education is vital for increasing literacy.
Government policies and international aid can contribute significantly to literacy improvements. Policies that support free primary education make schooling accessible to more children. International organizations often provide funding and expertise to support these initiatives. Their collaboration with local governments is essential for success. Together, these efforts create a supportive environment for learning.
Literacy Initiatives and Their Impact
Literacy initiatives in Tanzania are crucial for developmental progress. The government has implemented free primary education policies, making schooling more accessible. This move encourages more children to attend school, especially in rural areas. As a result, literacy rates among the youth have shown significant improvement. Free education policies give families hope for a better future.
Various non-governmental organizations (NGOs) also contribute to literacy initiatives. These organizations often focus on building schools and providing essential resources. For example, NGOs help supply books, uniforms, and other learning materials. According to many reports, these resources significantly enhance the quality of education. With better facilities, students are more likely to attend and excel in school.
Teacher training programs are another vital initiative. In Tanzania, the shortage of qualified teachers has been a persistent issue. Programs aimed at providing better training for teachers ensure students receive quality education. These programs often include workshops, courses, and practical training sessions. Well-trained teachers can offer more effective teaching, leading to improved literacy rates.
Community involvement plays an essential role in these initiatives. Educating parents and communities on the importance of literacy encourages greater support for education. Community awareness programs emphasize the long-term benefits of education. When parents understand the value of schooling, they are more likely to keep their children in school. This collective effort results in higher literacy levels and better opportunities for children.
International organizations also play a supportive role. They provide funding, expertise, and resources to bolster local initiatives. Collaboration between international bodies and the Tanzanian government amplifies the impact of these programs. By working together, they create a more robust educational framework. This partnership paves the way for sustainable literacy development in Tanzania.
Key Takeaways
- Tanzania’s adult literacy rate is around 77%.
- The literacy rate among youth is approximately 86%.
- Economic status significantly affects access to education.
- Government initiatives provide free primary education.
- Gender disparity exists with higher male literacy rates.

